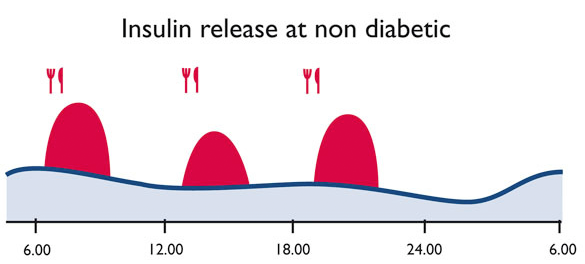
It is the target of the diabetes therapy to compensate completely for the primary malfunction of the carbohydrate metabolism. This goal can only be achieved if the person concerned is compliant.
In former times the person had to adapt to the therapy, today it is quite the opposite. The therapy is customized to the needs of an individual and his lifestyle.
It is important that especially people with type 2 diabetes change their lifestyle in terms of training activity and diet to achieve weight loss. In some cases this is enough for normalizing blood sugar levels. If these measures do not lead to success oral antidiabetic drugs are the next choice. Mostly in the beginning just one single substance is used.
If this is not sufficient the physician will prescribe a combination of different substances or even insulin to bring blood sugar down to the target range. Today it is a goal to deliver insulin similar to the physiological production.
These are the different types of therapy:
Prandial Insulin Therapy
People with diabetes performing Prandial Insulin Therapy administer regular insulin or short acting insulin analogues only when eating. This method is perfect for people with type 2 diabetes if their body produces enough basal insulin (for fasting condition). The proper dose of insulin is dependent on the blood glucose value before the meal and the planned intake of food or the peson administers a fixed dose of insulin following the advice of the physician. People do not suffer from restrictions regarding food or lifestyle and will therefore increase their quality of life level.
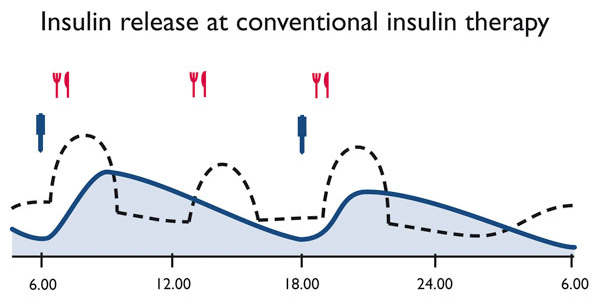
Performing Conventional Insulin Therapy the person with diabetes injects mixed insulin twice a day, morning and evening. In some cases it makes sense to administer mixed insulin three times a day, at breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Conventional Therapy is the best choice for people with regular daily routine who are able to take their meals at fixed times.
This is important because the combination of short and long acting insulin at fixed times requires regular intake of food to avoid hypoglycaemia.
The main advantage of the Conventional Therapy for the person concerned is that it can be easily performed due to the infrequent injections.
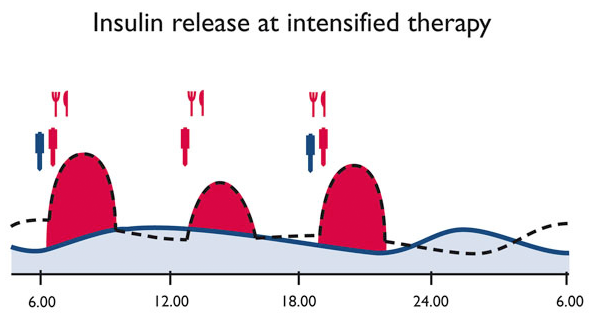
Intensified insulin therapy (ICT), Functional Insulin Therapy (FIT), Basis-Bolus-Therapy (BBT) – different names for modern types of insulin therapy when we try to copy the metabolic situation of healthy individuals by multiple daily injections and several blood glucose tests per day. Time and amount of food uptake can be chosen freely.
The principles of this therapy are the separate application of middle- to long acting insulin (morning and evening or morning, noon and late evening), to cover basal insulin need for 24 hours. Additionally the person concerned applies short-acting insulin to cover the need for insulin after meal or to correct for high blood glucose levels = bolus.
People with diabetes have to care about Injection/Meal-Distance which is depending on the used type of insulin between 0 (insulin analogue) and 30 minutes (regular insulin). ICT works well for people with type 1 diabetes, motivated persons with type 2 diabetes and pregnants. ICT enables the people to achieve good glycemic control with avoiding both hypo- and hyperglycemia. This kind of therapy allows an adaption to individual lifestyle. People performing this kind of therapy need an intensive training. They have to check blood glucose levels 4 -7 times a day, keep an accurate diary and they need to be willing to inject insulin several times a day.
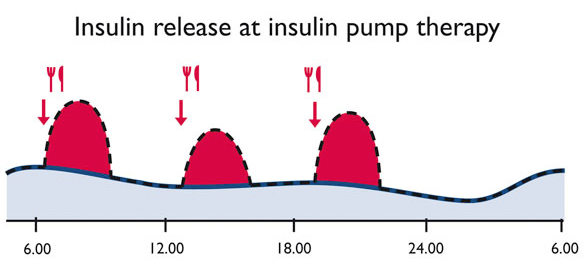
Another name for insulin pump therapy is CSII, meaning continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Insulin pump therapy allows a much better diabetes management as we are able to deliver insulin (regular insulin or short acting analogues) in very small pre-programmed increments for basal insulin needs around the clock.
This copies the physiological function of a healthy pancreas and blood sugar levels in a fasting state and between meals stays stable. Up to the individual needs of a person with diabetes insulin amounts can be programmed adapted to his needs. Insulin which is needed to cover meals is delivered precisely by an easy button press.
This allows people with diabetes to be absolutely flexible: doing sports, sleeping longer, enjoying life works perfects after an appropriate training on the pump. Medical indications for using an insulin pump are: fluctuations in blood glucose which cannot be controlled; Dawn-phenomenon, insulin resistency, hypoglycemia anawareness, frequent hypoglycemia, painful diabetic neuropathy, exercise and pregnancy.
More information:
Oral Antidiabetics
Insulin
Injection technique